Wirehand Wireless Frequently Asked Questions
What is fixed-wireless Internet service?

Wirehand Wireless is a fixed-wireless Internet service network. This type of network allows WCEC to provide reliable, high-speed Internet to rural areas not served by cable or fiber Internet networks. Your Internet service is broadcast from our main access point at the WCEC office to Wirehand Wireless transmission towers throughout our service territory and then on to each subscriber's individual locations. Internet is received at your location by a Wirehand Wireless antenna which is mounted on the outside of your home or business. This antenna has a built-in modem and is powered by a power supply located inside your location. The power supply also has ports that allow the signal received from the antenna to travel to your router. The router then sends the signal to devices at your location.
My Internet isn't working - what should I do?
STEP ONE: Power Cycle Your Equipment
It may seem trivial, but often the easiest solution is power cycling your equipment.
We recommend starting by power cycling your router.
NOTE: This DOES NOT mean to hold down the reset button on the router. This will reset your router's factory settings to default and you will need to set the router back up. If this happens, this link may help you set your router back up.
After power cycling your router, if your internet is still not working after 3-5 minutes, then power cycle your Wirehand Wireless antenna by unplugging the antenna's power supply inside your home or business. You do not need to leave it unplugged, you can simply unplug it and immediately plug it back in.
Keep in mind that power cycling any equipment takes 3-5 minutes to fully restore the connection.
Examples of Wirehand Wireless Antenna Power Supplies:




If you are having trouble locating your WCEC power supply, it is located near your router generally plugged into the same wall outlet or surge suppressor. You can trace the ethernet cable that runs from your router’s internet/WAN port back down to the power supply as well. Shown below is a picture of an ethernet cable plugged into the WAN port of a router:

STEP TWO: Verify the Status of Your Router
Routers come in many brands, shapes, and sizes, Shown above/below are some different brands and models of routers to help you locate yours.



All routers have the following indicator lights on them to help you verify the status of your router's connections.
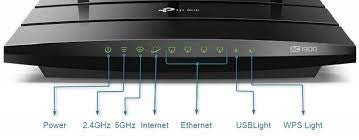
Typically, these lights are green or white to indicate working and red or orange to indicate a down status.
POWER LIGHT: If the power light is off, make sure that the router is connected to a wall outlet or power source.
2.4 GHz/5GHz LIGHTS: Most routers today are dual-band routers, which means they operate on two frequencies that you can connect your devices to. As a general rule, connect the closest devices to your router to the 5 GHz frequency and the further devices and devices that move (i.e. phones) to the 2.4 GHz frequency. These network names will show up when you connect any device to your WiFi as something like Netgear69 and Netgear69_5GHz. If either of these lights are off or orange/red, your WiFi signal is not being broadcast. Check the back of your router for an on/off switch or login to your router's settings to make sure the WiFi broadcast settings are on. This link may help you to turn your WiFi broadcast on/off. (See below for how to access a typical router's settings.)
INTERNET LIGHT: If the Internet light is off or is orange/red, you are not receiving a signal from your Wirehand Wireless antenna. First, power cycle your equipment as instructed in STEP ONE. If this does not work, you can try to bypass your router by connecting your internet ethernet cable directly from your antenna's power supply to a computer at your home. Disconnect the ethernet cable from the router's WAN/Internet port and connect it directly from the antenna power supply to a computer. If the Internet works when the router is bypassed, there is a problem with your router's WAN/Internet port that is prohibiting Internet traffic from being accessible.
NOTE: Not all laptops will have ethernet ports as newer models only have WiFi capabilities.
Some of our members have a PPPoE connection that requires a username and password to connect when bypassing the router. Please call our office at 979-543-6271if this is the case.
If the above does not work, there is most likely an Internet outage to your transmission tower or to the main access point at the WCEC office.
ETHERNET LIGHTS: Ethernet lights indicate the status of any devices connected to your router with an ethernet cable.
STEP THREE: Contact WCEC Wirehand Wireless Technicians
If your internet is still not working after STEPS ONE and TWO, please call the WCEC Office during normal business hours to speak with a technician. After hours, our after-hours dispatch center will take your information and relay it to an on-call technician. The technician will contact you as soon as possible.
However, if there is a major Internet outage, our technicians may be working to resolve the issue and a callback may be delayed. Dispatch should notify you of the outage when you call. Major outages are generally reported on our Facebook and Instagram pages as well.
How do I access my router's settings?
Launch a web browser from a computer or mobile device that is connected to your router's network or connected directly to the router with an ethernet cable.
Depending on your router's brand, you will enter either routerlogin.net, tplinkwifi.net, or linksyssmartwifi.com. You can also enter the default IP for most routers which is 192.168.1.1. You may need to consult your router’s setup to find out the router’s default IP address.
Enter the router user name and password. Typically, the user name is admin. Default passwords are usually: Password1, admin, password, or blank. If you changed your router’s username and password during setup, log in with that username/password combination. If you have forgotten, use the router's password recovery method, or factory reset your router and go through the initial setup again.
My Internet is slow - why?
There are a number of factors that can affect your network's speed. Here are a few explanations.
Are there any range extenders on the network? Are you connected to one?
Range extenders can be beautiful things. As the name suggests, they help extend the WiFi signal from the router to parts of the house that are too far for the router to cover. However, extenders on the network can also cause unforeseen connectivity issues, often due to a poor connection between the router and the extender itself. If that connection is poor, any devices connected to the range extender will also experience issues. Like routers, there are a few red flags to look for when it comes to range extenders, including age, price, and specifications.
Are all devices on the network experiencing connection issues?
Sometimes, a member will call in concerned about slow speeds, but their speed test results will show nothing out of the ordinary. In those cases, the issue likely isn’t their home network, but the device itself. At this point, the next step would be to determine if any other devices on the network are experiencing similar connection issues. If they’re not, then this specific device is most likely the problem.
How far away is the router? Are there any walls or other obstructions in the way?
Distance from the router matters. If a device is too far away from the router, it will inevitably begin to experience connection issues like slow speeds. Wireless routers typically only cover between 150 and 300 feet—roughly the size of a single-family dwelling. Physical obstructions (like walls) between the router and the customer’s device can also shorten this coverage area even more.
Is anyone else using the WiFi right now?
The number of devices connected to your router can affect the speed of the connection. When only a few people are connected, traffic flows smoothly; but when too many devices are in use at once, this leads to a ton of issues, including slow internet and buffering video.
Where is my internet modem?
The short answer is you don’t have one. Your modem is built into our wireless antenna that connects you to one of our transmission towers. Therefore, when you bypass the router and plug your device directly into our power supply, you are essentially plugging directly into your “modem”.
